- Have any problems?
- sales@anankafasteners.com
Fastener Failure : 5 Common Causes and How to Prevent Them
As a leading fastener manufacturer and supplier in India, Ananka Fasteners understands that fastener failures can result in catastrophic consequences for construction, automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. Whether it’s a loosened bolt on a wind turbine, corrosion eating away at marine fasteners, or a fractured bolt under cyclic loading, fastener failures compromise structural integrity, safety, and project timelines. This comprehensive guide explores the five most common fastener failure modes, their underlying causes, and proven prevention strategies to ensure your bolts, nuts, and industrial fasteners perform reliably throughout their operational life.
Table of Contents
ToggleFastener failures are far more common than many engineers and contractors realize. Studies indicate that fasteners account for a significant portion of mechanical failures in industrial settings, particularly in high vibration environments like wind turbines and automotive systems. The consequences range from minor equipment downtime to catastrophic structural collapse, making failure prevention not just an economic imperative but a safety necessity.
At Ananka Fasteners, we’ve seen how proper fastener selection, installation practices, and maintenance protocols can eliminate these failures entirely. The key is understanding the root causes and implementing the right preventive measures at every stage from design and manufacturing through to installation and ongoing inspection.
Fastener Corrosion: Environmental Attack on Your Assembly
Corrosion represents the leading cause of fastener failure, particularly in outdoor, marine, coastal, and chemically aggressive environments. When fasteners corrode, they lose mechanical integrity, become brittle, and ultimately fail under load.
How Corrosion Causes Fastener Failure
Corrosion occurs through direct chemical attack and electrochemical corrosion. Electrochemical corrosion often results from galvanic action (two dissimilar metals in contact) or stress corrosion cracking (tensile stress combined with a corrosive environment).
The mechanisms of corrosion-induced failure include:

Loss of mechanical integrity, causing failure under normal stress.
Fatigue acceleration, as corrosion sites act as stress concentrators.
Compromised joint clamping force due to material loss around the fastener head.
Prevention Strategies for Corrosion
- Material Selection: Choose materials like Stainless Steel Grade 316 for marine applications, or Inconel/Hastelloy for extreme chemical environments.
- Protective Coatings: Apply coatings like Hot dip galvanizing (for long-term structural protection) or Zinc nickel plating (superior for high stress aerospace use). Dacromet coatings offer excellent salt spray resistance and are free of hydrogen embrittlement.
- Dielectric Barriers: Prevent galvanic corrosion when joining dissimilar metals by using isolating washers.
Vibration-Induced Loosening: The Silent Failure Mechanism
Fastener loosening due to vibration and dynamic loads is a prevalent failure mode in automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery. A loosened fastener gradually loses its clamping force, leading to joint separation and eventually catastrophic failure.
Why Vibration Causes Fasteners to Loosen
Loosening is caused by:
Cyclic shear stress (vibrations applying repeated transverse forces) leading to micro-slipping between mating threads.
Thermal cycling which promotes loosening due to differential expansion and contraction.
Insufficient initial torque which leaves fasteners highly vulnerable to movement.
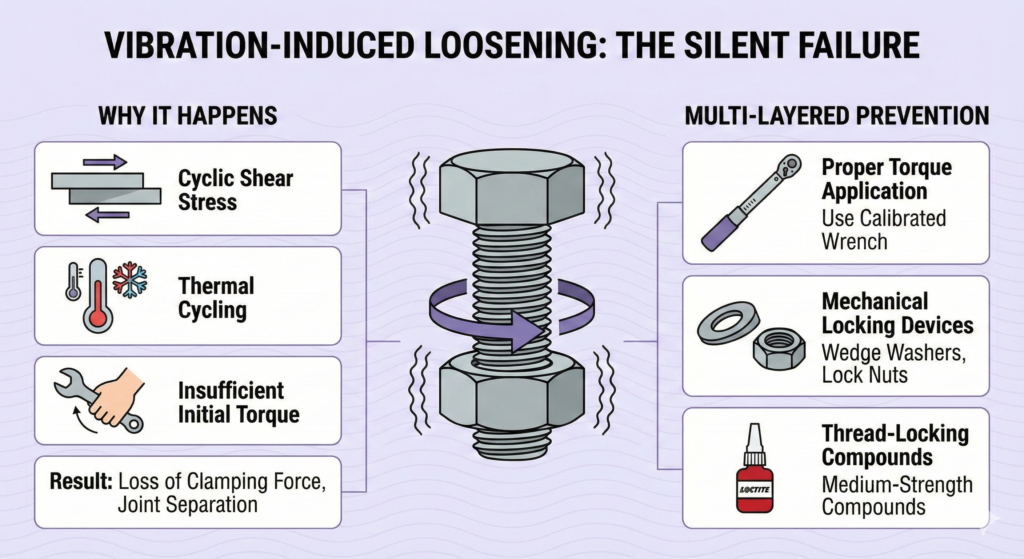
Multi-Layered Prevention Approach
- Proper Torque Application: Always use a calibrated torque wrench and consult manufacturer recommendations. Be aware that torque wrench accuracy typically ranges from ±17% to ±23%.
- Mechanical Locking Devices: Use solutions that rely on mechanical principles, such as wedge locking washers or all thread locking nuts (like HARDLOCK nuts), which engage all threads. Nylon-insert lock nuts (Nylock) are suitable for many, but not all, vibration environments.
- Thread-Locking Compounds: For critical assemblies, use medium-strength compounds (e.g., Loctite 243) that cure to fill the voids between threads, resisting rotational movement while still allowing for maintenance disassembly.
Fastener Fatigue Failure: Cumulative Stress Leads to Sudden Fracture
Fatigue failure occurs when fasteners are subjected to repeated cyclic loading, causing progressive material damage and eventual brittle fracture. Unlike overload failures, fatigue cracks develop silently and can fail suddenly under normal operating loads.
Recognizing Fatigue Failure Mechanisms
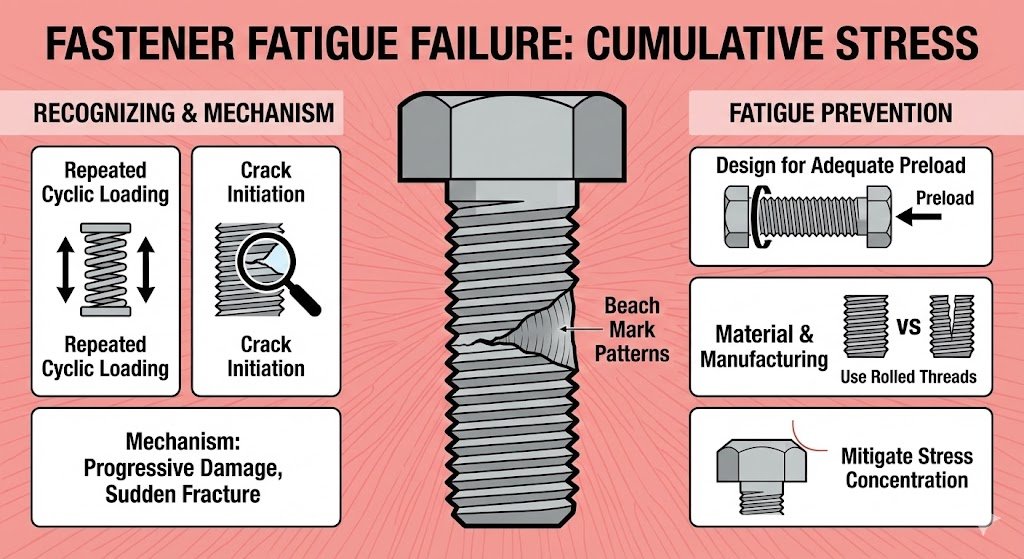
Beach mark patterns: The fractured surface shows wave-like “beach marks” originating from a stress concentration point.
Crack Initiation: Fatigue cracks typically start at stress concentration points near the root of the threads.
Corrosion Fatigue: The combination of corrosion and cyclic loading drastically reduces fatigue strength, causing failure at significantly lower stress levels.
Fatigue Prevention Strategies
- Design for Adequate Preload: Sufficient initial preload (clamping force) is the single most important prevention measure against fatigue failure. Inadequate preload is the primary cause of these failures.
- Material Selection & Manufacturing: Specify rolled thread fasteners, which offer 20-30% higher fatigue strength compared to cut-thread fasteners due to superior grain flow.
- Mitigate Stress Concentration: Eliminate sharp corners and use larger fillet radii under the bolt head in the assembly design.
- Corrosion Control: Implement corrosion prevention measures, as corrosion fatigue dramatically reduces a fastener’s service life.
Thread Stripping and Over-Tightening Damage
Thread stripping occurs when excessive torque damages the helical grooves, compromising joint integrity. This failure can result in loss of clamping force or complete joint failure if the fastener backs out.
How Thread Stripping Happens
Over torquing: Using impact drivers without torque control or manually over-tightening can exceed the material’s limits and damage threads.
Mismatched components: Installing metric fasteners into imperial holes (or vice versa) causes cross-threading.
Poor quality fasteners or poor thread quality in soft base materials (like aluminum).
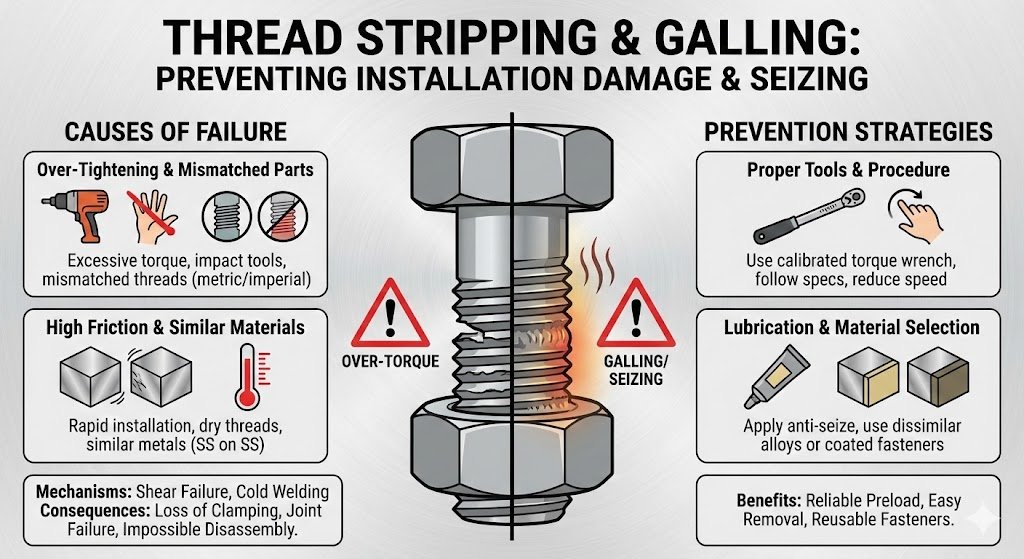
Prevention Through Installation Best Practices
- Use Calibrated Torque Tools: Always use a calibrated torque wrench set to precise manufacturer specifications. Never use impact wrenches for critical fasteners.
- High Quality, Certified Fasteners: Source fasteners with material traceability from ISO 9001 certified suppliers.
- Substrate Reinforcement: When fastening into soft metals, use Helicoil thread inserts to reinforce the fastener hole and increase the thread engagement area.
- Thread Inspection: Before installation, inspect threads visually and use go/no-go gauges for critical applications to ensure compliance with standards like ISO 898-1.
Galling and Seizing: Preventing Metal-to-Metal Adhesion
Thread galling (seizing) occurs when metal surfaces cold-weld together during installation, causing the fastener threads to lock up and preventing proper installation. This is common with ductile, work-hardening materials like stainless steel and titanium.
Why Galling Happens
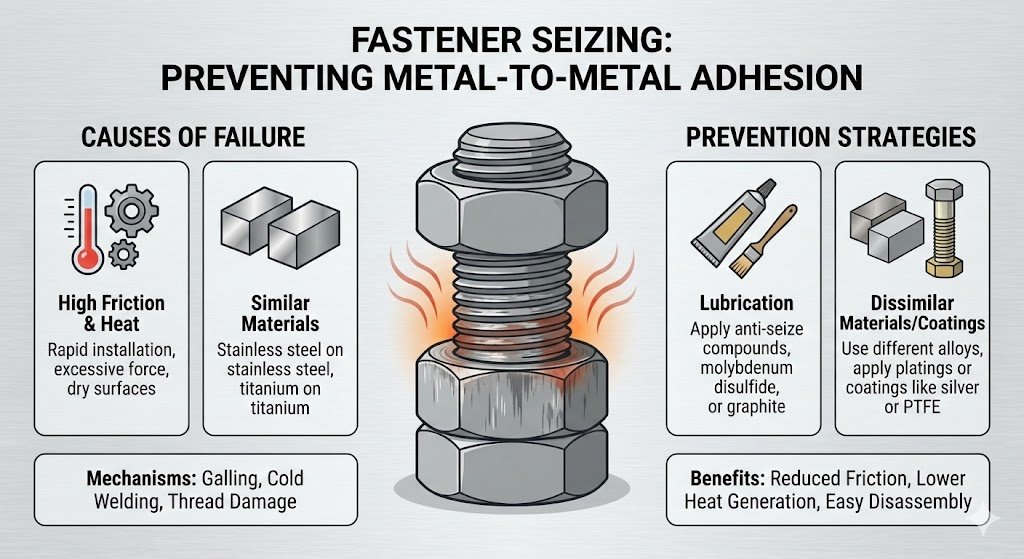
Friction-generated heat: Fast tightening speeds create temperature spikes that soften the metal surfaces.
Micro-welding: Metal particles transfer between the mating surfaces, causing cold-welds that prevent further rotation.
Over-tightening: Excessive torque forces mating surfaces together under high pressure, accelerating galling.
Comprehensive Galling Prevention Strategy
- Lubrication The First Line of Defense: Apply an anti seize lubricant to thread surfaces before installation to reduce the coefficient of friction and lower heat generation.
- Installation Technique: Reduce installation speed to allow heat dissipation. Avoid rapid, friction-induced heating.
- Material Selection: Where possible, use two different material grades (one softer, one harder) to reduce the tendency for material adhesion.
- Pre-Installation Prep: Inspect and clean fastener threads with compressed air to remove debris that significantly increases galling risk. Use coarse-pitch threads where feasible.
Quality Control and Inspection: Preventing Failures Before They Start
Robust quality control during manufacturing and careful inspection during installation prevent many failures. At Ananka Fasteners, we maintain rigorous quality standards:
- ISO 898-1 for metric bolt specifications.
- ISO 16047 for torque-tension testing requirements.
- ISO 9001 for quality management systems.
Pre-Installation Inspection Checklist:
- Verify fastener grade, size, and coating match specifications.
- Inspect threads visually for damage or defects.
- Confirm fasteners come from certified suppliers with material traceability.
- Verify documented torque specifications and installation procedures.
As India’s leading fastener manufacturer and supplier, Ananka Fasteners manufactures high-tensile bolts, stainless steel fasteners, and specialty fasteners engineered to withstand the demands of your toughest applications. The key to fastener success is a systems approach: start with properly specified fasteners from a reliable supplier, use correct installation techniques, and implement regular inspection protocols throughout the fastener’s life.
Fastener failures are preventable. Contact Ananka Fasteners today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure your projects benefit from our expertise.

About us
We are expert in manufacturing of customized fasteners. In the past 10 years we have helped 240+ customers across 40 countries to generate a revenue of 30,000 crores by delivering more than 30,000 SKU units.
We also manufacture, supply, export our wide range of Nuts, Bolts, Screws, Rods, Washers, Inconel Fasteners, Monel Fasteners, Hastelloy Fasteners, Nickel Fasteners, Carbon Steel Fasteners, Stainless Steel Fasteners, Inconel Fasteners from Mumbai to different parts of countries and continents. With the help of highly trained staff and the latest manufacturing equipment, we manufacture the best quality fasteners. Our high-quality fasteners are used in industries worldwide.
